Architecture
Probato was designed with a modular and highly extensible architecture to support functional-level test automation in an efficient and scalable way. The architecture adopts modern software design concepts, such as the Page Object Model (POM) and annotation-based dependency injection, enabling the creation of reusable, maintainable, and evolvable test scripts.
This approach ensures clear separation of responsibilities, predictable execution, and flexibility to adapt to different automation scenarios.
Architectural principles
The Probato architecture is based on:
- Modularity
- Isolation of responsibilities
- Component reuse
- Extensibility without impact on the core
- Transparent integration with external tools
These principles guide all layers of the framework.
Architectural layers and responsibility isolation
The Probato architecture is composed of multiple layers, each with well-defined responsibilities, facilitating maintenance, evolution, and fault diagnosis.
Interaction layer (Page Object Model)
- Implements the Page Object Model (POM) pattern, encapsulating user interface interaction logic.
- Each page, screen, or component is represented as an object containing methods for possible interactions (clicks, data entry, validations, etc.).
- Promotes code reuse and simplifies maintenance when the application interface changes.
Test layer (Scripts and Procedures)
Tests are organized into scripts, composed of actions divided into:
- Preconditions
- Procedures
- Postconditions
This separation helps isolate failures and precisely identify at which stage an error occurred.
Data injection layer
- Enables flexible and dynamic use of input data.
- Supports data injection via CSV files.
- Provides planned future support for JSON, YAML, and databases through custom plugins.
Persistence layer and database connectors
- Provides an integrated SQL and NoSQL executor capable of connecting to multiple databases.
- Allows defining database preconditions, dynamically changing states before tests, and restoring states after execution.
Annotation-based dependency injection
- Adopts a dependency injection model via Java annotations, promoting Inversion of Control (IoC).
- Simplifies manual configuration by allowing required objects to be injected automatically.
- Promotes modularity, decoupling, and component reuse.
JUnit 5–based execution model
Probato integrates with the JUnit 5 lifecycle, using dynamic tests and the @TestFactory annotation to generate test cases at runtime.
Execution Lifecycle
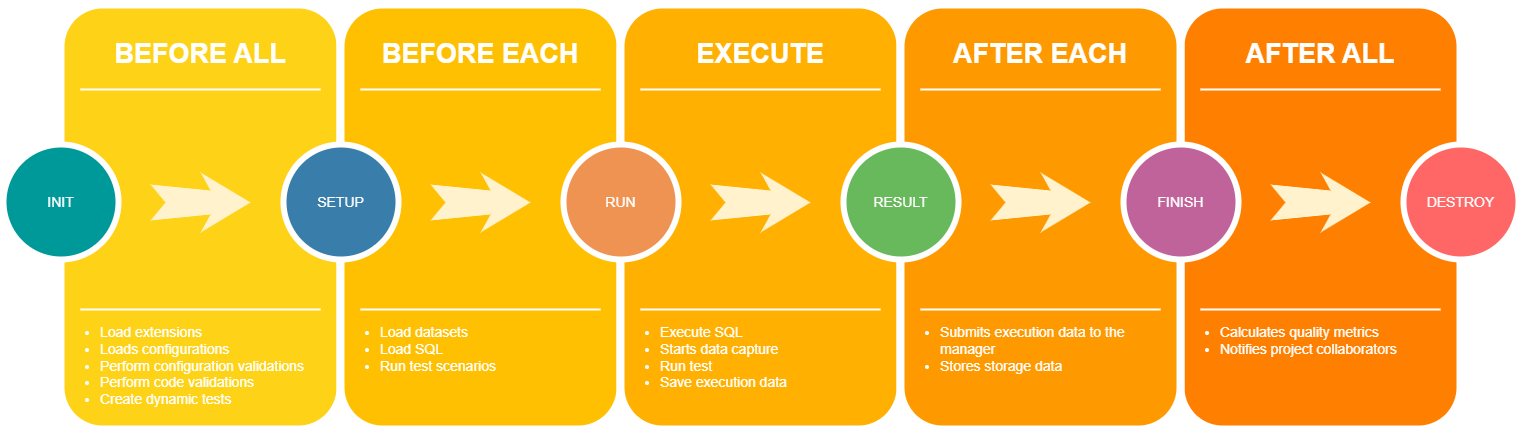
-
BeforeAll
Loads extension points, configurations, and performs code and environment validations. It also creates JUnit 5 dynamic tests. -
BeforeEach
Loads required datasets and scripts and initiates scenario execution. -
TestFactory
Dynamically generates tests based on scripts, procedures, and Page Objects. Supports data-driven testing, enabling multiple executions with different datasets. -
AfterEach
Submits collected execution data to Probato Manager and stores images and videos in the configured storage. -
AfterAll
Calculates software quality metrics and notifies collaborators about execution completion.
Multi-browser execution support
- Built on top of Selenium and Playwright APIs, enabling automation across multiple browsers.
- Extensible support for additional browsers, operating systems, and execution contexts.
Extensibility and plugins
- The framework was designed to be highly extensible, allowing new features to be added without modifying the core.
- Plugin support includes:
- New browser drivers
- Additional input data formats
- New validation types
- Custom SQL or NoSQL executors
Execution management and data collection
During test execution, Probato captures and processes data such as:
- Execution logs
- Screenshots
- Videos
- Executed steps
This data is sent to an integrated web application that provides:
- Centralized execution monitoring
- Detailed report generation
- Bug tracking
- Version-based analysis
The Probato architecture allows integration with external test management and defect tracking tools, such as TestLink and Mantis Bug Tracker, through its extensibility points. These integrations can be implemented as plugins without requiring changes to the framework core.
Advanced configuration and customization
Probato offers advanced configuration options for:
- Defining timeouts and intervals between actions
- Adjusting image and video capture quality
- Controlling execution across multiple monitors
Notifications and continuous integration
- Automatic notifications are sent to collaborators after each test execution.
- Integration with CI/CD tools, such as Jenkins, enables full automation of test processes within the development lifecycle.